人工智能在实验室安全管理中的应用、
挑战及应对策略
Applications, challenges, and coping strategies of artificial intelligence in laboratory safety
作者单位
柳长峰,王 睿
中国地质大学(北京)海洋学院,北京 100083
LIU Changfeng, WANG Rui
School of Ocean Sciences, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China
作者简介:
柳长峰(1982—),男,山西吕梁,博士,副研究员,主要研究方向为实验室管理与实验教学。
以下为本文目录结构
点击图片查看大图
摘 要
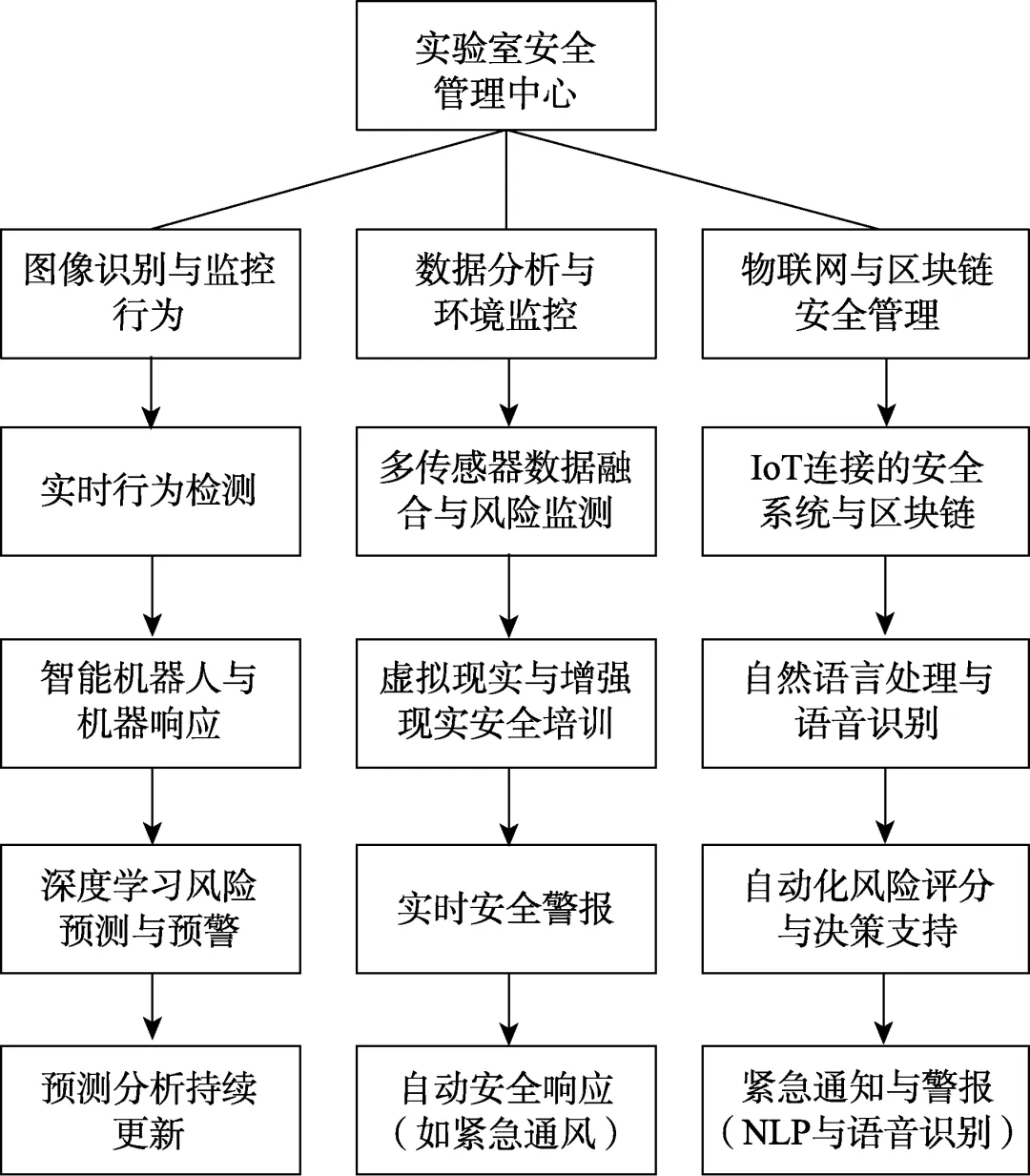
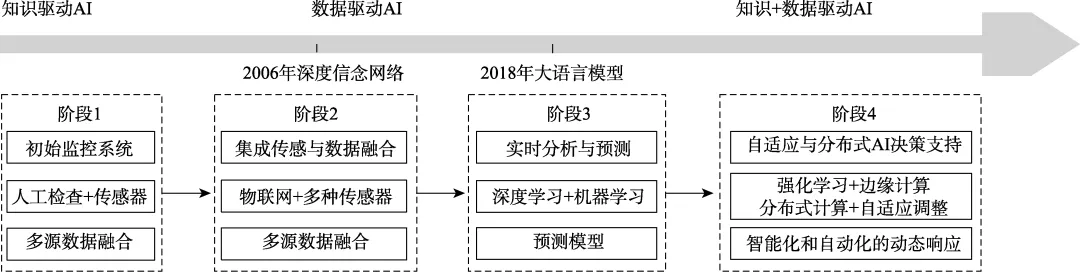
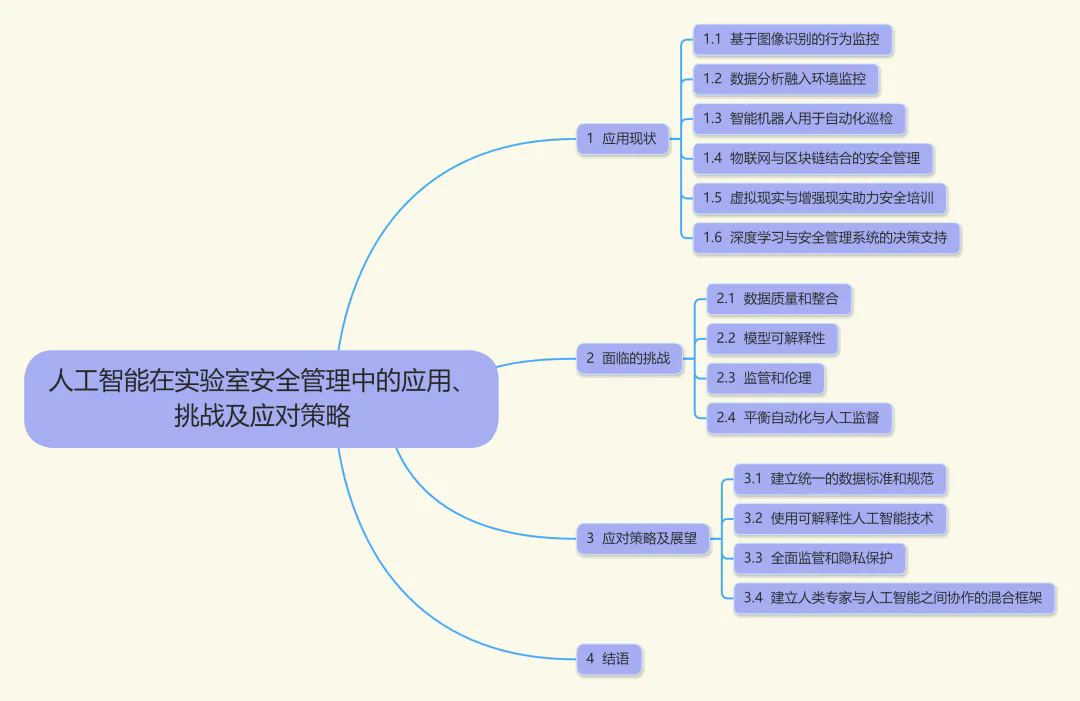
随着人工智能技术的迅速发展,实验室安全管理迎来了新的变革。该文系统探讨了人工智能技术在实验室安全管理中的多维应用,包括图像识别、数据分析、智能巡检机器人、虚拟现实和增强现实(VR/AR)培训、物联网与区块链的数据管理等。通过分析实际应用案例,总结了人工智能在实验室安全管理中的优势和挑战。在此基础上提出了应对策略:建立统一的数据标准和规范,提高数据质量;应用可解释性人工智能技术,增强模型透明度;构建全面监管和隐私保护框架,确保合法合规与伦理道德;建立人类专家与人工智能协作的混合框架,充分发挥二者优势。随着技术不断进步和策略有效实施,人工智能将推动实验室安全管理迈向智能化、自动化、数据化的新阶段,为科研活动创造更安全、高效的环境,助力科学研究持续健康发展。
Abstract: [Objective] The overarching objective of this research endeavor is to conduct an exhaustive and in-depth exploration of multifaceted applications, concomitant challenges, and the corresponding countermeasures to artificial intelligence (AI) within the domain of laboratory safety management. In the contemporary scientific landscape, laboratories are the epicenters of cutting-edge research and experimentation, often dealing with hazardous substances and complex procedures. Therefore, the prime focus is to ascertain how AI technologies can be optimally harnessed to fortify the safety and security infrastructure of these laboratories, thereby safeguarding the well-being of personnel, protecting valuable research assets, and ensuring the integrity of the scientific process. [Methods] To actualize this objective, meticulous and comprehensive review and analysis were carried out. This involved scouring a vast and diverse array of relevant literature sources, including peer-reviewed academic research papers, industry white papers, technical reports, and case studies. Simultaneously, an in-depth examination of real-world applications of AI in laboratories across a spectrum of scientific disciplines was conducted. By collating and synthesizing data from these multiple sources, valuable insights and empirical evidence were amassed regarding the practical implementation and effectiveness of AI in enhancing laboratory safety. [Results] The research findings reveal that AI has made substantial advancements in laboratory safety management. In image recognition, the algorithms of the Engineering Training Center of the University of Science and Technology Beijing are capable of facial recognition and authentication of experimental personnel, as well as the recognition and early warning of dangerous behaviors, effectively reducing the risk of human errors during the experiment process. The Electrical and Electronic Experimental Teaching Demonstration Center of Central China Normal University applies Internet of Things (IoT) technology. By identifying and responding to abnormal situations, it brings great convenience to the management work of the laboratory. The intelligent robots in the laboratory of Tianjin Polytechnic University detected fire hazards during unattended periods. The virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technologies in many universities have enhanced the safety awareness and emergency response capabilities of trainees. Tsinghua University utilizes technologies such as the Internet and the Internet of Things to track the full-life cycle status of controlled chemicals. It can grasp the usage amounts and stock quantities of controlled chemicals in different laboratories in real time, thereby eliminating potential hazards caused by irregular storage and use in laboratories. Data quality and integration issues due to inconsistent collection methods and format variations impacted AI model performance. The “black-box” nature of some AI models makes it difficult for the laboratory staff to understand and trust them. Regulatory and ethical concerns exist as current safety standards do not account for AI, and privacy issues are involved. Moreover, finding the right balance between automation and human supervision is crucial, as laboratories are complex and dynamic environments. AI lacks contextual awareness and adaptability, while overreliance on it could lead to human skill degradation. Therefore, establishing effective communication channels between AI and humans is essential to ensure the highest level of laboratory safety. [Conclusions] AI holds great promise and potential in revolutionizing laboratory safety management. The diverse applications of AI technologies, as demonstrated by various case studies and examples, show their capacity to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and responsiveness of laboratory safety measures. However, to fully realize this potential, concerted efforts are required to address identified challenges. Strategies such as the establishment of unified data standards and specifications, application of interpretable AI technologies, construction of comprehensive regulatory and privacy protection frameworks, and development of collaborative frameworks between human experts and AI systems are crucial. By implementing these measures, the laboratory safety management landscape can be propelled toward a new era of intelligence, automation, and datafication. This will not only create a safer and more efficient environment for scientific research activities but also contribute to the sustainable and healthy development of the scientific community as a whole.
关键词:人工智能;实验室安全;图像识别;数据分析;智能巡检
Key words: artificial intelligence; laboratory safety; image recognition; data analysis; intelligent patrol
以下进入全文阅读
引文格式:柳长峰,王睿. 人工智能在实验室安全管理中的应用、挑战及应对策略[J]. 实验技术与管理, 2025, 42(4): 239-244.
Cite this article: LIU C F, WANG R. Applications, challenges, and coping strategies of artificial intelligence in laboratory safety[J]. Experimental Technology and Management, 2025, 42(4): 239-244. (in Chinese)
《实验技术与管理》2025年04期P239-244
DOI: 10.16791/j.cnki.sjg.2025.04.031